This site is intended only for the use of UK Healthcare Professionals
Podcast
With a dynamic and practical content absorption format, this section covers the main topics featured on the website, including healthcare management subjects.
Our channels

Season 1
Here you can find all the episodes of our first season with health care professionals.
Learn more
Season 2
Here you can find all the episodes of our second season with health care professionals. Every week a new episode.
Learn more
Season 3
Here you can find all the episodes of our third season with health care professionals. Every week a new episode.
Learn moreInformation for Healthcare Professional Use Only In this episode of the Inside Medical Nutrition podcast, Dr. Linia Patel interviews dietitians Jamie Leung and Sam Ogundere about blended diets in transitional care. Jamie and Sam discuss their roles supporting patients needing enteral feeding, as they observe an increasing number of adults requiring blended diets. They highlight the variety of conditions necessitating enteral feeding tubes, including stroke, MND, Parkinson's, and cancer. The conversation explores the use of homemade blended diets, with Jamie estimating that around 5% of their paediatric caseload relies entirely on blended diets, while 30% use them partially. They share positive experiences regarding tolerance and the natural inclination of parents to blend familiar foods. Challenges include inconsistent support from schools and the resource demands of administering blended diets. The discussion shifts to tube feeds with food-derived ingredients, which both dietitians embrace as a valuable option, particularly for parents with limited time, small kitchens, or financial constraints. They acknowledge that awareness of these options is still growing, and that initial management often focuses on medical solutions. Jamie and Sam emphasise the importance of open-mindedness, flexibility, and parental involvement in blended diet management. They recommend the EPSGHAN guideline for children and the BDA toolkit as helpful resources. The need for risk assessment forms, information leaflets, and nutritional analysis programs is also highlighted. Finally, they discuss transitional care, emphasising the crucial role of multidisciplinary teamwork and communication. They stress the importance of a joint visit to ensure a smooth handover and address any concerns. The podcast concludes with a call for continued research and greater awareness of blended diets for patients requiring enteral nutrition. Listen to the full podcast episode to learn more about blended diets in transitional care and how best to support patients requiring enteral feeding.
Information for healthcare professional use only. In this episode of the Inside Medical Nutrition podcast, Dr. Linia Patel interviews Professor David Wright and Jan Flynn about improving medication administration for people with dysphagia. The conversation highlights the challenges faced by patients with dysphagia around swallowing medication, particularly tablets. Therefore, emphasising the importance of considering dysphagia when prescribing medications in dysphagia management. David stresses the need to first assess whether the medication is still necessary and effective. If so, alternative routes (e.g. patches) and formulations should be explored before resorting to crushing tablets. Both experts caution against routinely crushing tablets, as it can alter drug release, cause side effects, and increase the risk of medication errors. They highlight the complexities of liquid medications, including stability issues and the potential for interactions with thickeners used for dysphagia management. Both experts share their own professional experience of supporting patients with dysphagia and the challenges they have faced with the medicine management in this patient group. Examples of projects and addressing knowledge gaps in this area of dysphagia management are also shared. The podcast concludes with a call for greater awareness and education among healthcare professionals regarding dysphagia and medication administration. They emphasise the need to prioritise patient safety and quality of life by carefully considering medication options and seeking expert advice when needed. Listen to the full podcast episode to learn more about administering medication to patients with dysphagia. To learn more about thickening drinks for dysphagia, watch this video.
Information for Healthcare Professional Use Only In this episode of the Inside Medical Nutrition podcast, Dr. Linia Patel speaks with Mikayla Profe-Fuchsloch, a dietitian and assistant professor at the University of Coventry, about the impact of fibre inclusion in enteral nutrition for paediatric patients. Fibre, which is classified by solubility, viscosity, and fermentability, increases stool weight, improves bowel regularity, and can balance stool frequency in both diarrhoea and constipation cases. All these features make it a useful addition to enteral nutrition. It is not uncommon when managing paediatric patients with complex medical needs to have issues related with the gastrointestinal system. There can be issues with gut dysmotility and symptoms such as gastroesophageal reflux, delayed gastric emptying, diarrhoea and constipation. In clinical practice, adding in a fibre supplement or choosing a fibre containing enteral feed can help to manage these issues. Current guidance from the European Society of Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition on how much fibre per day paediatric patients require recommends an increased fibre intake in children with neurodisabilities of 17-21g of fibre per day.1 This may be provided by the fibre from an enteral feed as well as the addition of a fibre supplement. Fibre supplements that are partially hydrolysed, such as Partially Hydrolysed Guar Gum (PHGG), which can help to improve bowel motions1. PHGG has been shown to work as a prebiotic, supporting the growth of beneficial gut bacteria2,3,4. In addition, the combination of peptide-based feeds and fibre can help to improve tolerance and gastrointestinal symptoms. Mikayla shares a case study where PHGG fibre supplementation significantly improved bowel motions and reduced medication reliance in a child with complex clinical conditions. She stresses the importance of a gradual introduction of fibre, monitoring tolerance through detailed symptom diaries, and involving parents in the decision-making process. She also points out the lack of standardised tools for fibre introduction, emphasising individualised approaches. Listen to the full podcast episode to learn more about fibre inclusion in enteral nutrition and the role it plays. 1. Romano C, van Wynckel M, Hulst J, et al. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2017;65:242–264 2. Ohashi Y, et al. Benef Microbes 2015;6(4):451-455. 3. Yasukawa Z, et al. Nutrients 2019;11(9):2170. 4. Reider SJ, et al. Nutrients 2020;12(5):1257.
Information for Healthcare Professional Use Only In this episode of the Inside Medical Nutrition podcast, Dr. Linia Patel interviews Smruthi Venkat, a speech and language therapist (SLT) specialising in stroke rehabilitation. They delve into the complexities of dysphagia, swallowing difficulties commonly experienced by stroke patients. Smruthi explains that stroke patients present with varying swallowing impairments depending on the location of the stroke. These can include oral motor weakness, sensory deficits affecting the ability to distinguish food temperatures or detect residue, and impaired coordination of the four-stage swallowing process. The conversation highlights the importance of early swallow screening for stroke patients upon hospital admission. If difficulties are detected, a specialist assessment by a speech and language therapist is crucial. This bedside swallowing assessment involves a detailed case history, cranial nerve and oral motor examination, and observation of the patient consuming different food and fluid textures. Smruthi emphasises the role of the International Dysphagia Diet Standardisation Initiative (IDDSI) framework in determining safe food and fluid textures. If a patient is deemed unsafe or silent aspiration is suspected, further instrumental assessments like video fluoroscopy or endoscopy are recommended. The podcast also explores the Eating, Drinking, and Swallowing Competencies Framework developed by the Royal College of Speech and Language Therapists (RCSLT). These competencies provide standards for knowledge, skills, and understanding for professionals supporting individuals with eating and drinking difficulties. Smruthi shares how these competencies have informed training programs and improved the quality of care for dysphagia patients. Finally, the discussion covers stroke rehabilitation guidelines, emphasising the potential for patients to benefit from rehabilitation at any point after their stroke. Smruthi outlines various rehabilitation options, including texture modification, behavioural therapy, and exploratory muscle strength training. She underscores the importance of a collaborative, multidisciplinary team approach involving physicians, nurses, therapists, dietitians, and psychologists to support the patient's recovery journey. Smruthi highlights the importance of oral hygiene for stroke patients, following SLT recommendations, and stroke rehabilitation. Listen to the full podcast episode to learn more about dysphagia and how dysphagia is managed in stroke rehabilitation patients.
Information for Healthcare Professional Use Only In this episode of the Inside Medical Nutrition podcast, Dr. Linia Patel interviews Marie Watson, a paediatric specialist dietitian, about her experience managing enteral nutrition patients in the community. Marie shares her journey into dietetics and her passion for working with children. Marie shares her knowledge about peptide feeds compared to whole protein enteral feeds and the clinical benefits of these types of feeds. Peptide feeds are commenced in response to poor tolerance to whole protein enteral feeds. Marie outlines the process of transitioning patients to peptide feeds, emphasising a slow, gradual approach to monitor for adverse effects such as worsening tolerance/gastrointestinal symptoms. She notes that while most patients experience improved symptoms, it is crucial to be prepared to revert to whole protein feeds if necessary. The discussion explores the use of low-calorie peptide feeds for patients prone to excessive weight gain, highlighting the importance of achieving adequate protein and micronutrient intake while managing calorie levels, helping to overcome the challenges of balancing feed volume and tolerance with meeting nutritional needs. Examples of the use of peptide feeds in clinical practice are also discussed. Marie stresses the significance of a multidisciplinary team approach, involving gastroenterology consultants and tube feeding nurses, to provide comprehensive care for enteral nutrition patients. The conversation touches on the challenges of working in this field, including funding constraints and the need for ongoing education and support for dietitians. Marie emphasises the importance of staying informed about available products such as peptide feeds and being open to trying different approaches to manage patients with complex nutritional needs. Finally, Marie encourages healthcare professionals to reach out to experienced colleagues for guidance and support, recognising that each patient is unique and requires individualised care. The podcast concludes with a call for continued research and innovation in the field of enteral nutrition to improve outcomes for children with enteral feeding tubes. Listen to the full podcast episode to learn more about managing patients with enteral feeding tubes in the community using peptide feeds.
Information for Healthcare Professional Use Only In this episode of the Inside Medical Nutrition podcast, Dr. Linia Patel interviews Harriet Farr, a paediatric home enteral feeding dietitian, about navigating blended diets on a budget amidst the current cost of living crisis. Harriet shares her journey into dietetics and her passion for supporting children requiring tube feeding. The conversation begins with a definition of what is a blended diet, emphasising the use of real food ingredients blended to a suitable consistency for administration via gastrostomy tubes. Harriet also mentions commercially made feeds with food-derived ingredients. She then delves into the practical aspects of supporting families on blended diets, including liaising with medical teams, providing information on benefits and potential problems, and ensuring safe preparation and administration. A significant portion of the discussion focuses on the impact of the cost-of-living crisis on families using blended diets. Harriet acknowledges the financial strain and the reluctance of parents to discontinue blended diets due to the positive impact on their children's gastrointestinal symptoms. She emphasises the importance of dietitians being aware of these challenges and offering practical solutions. Harriet provides several budget-friendly tips, such as utilising more affordable protein sources like beans and lentils, which also offer added fibre. She suggests considering frozen fruits and vegetables and batch cooking to reduce costs and time. Harriet also highlights the importance of menu planning, shopping lists, and buying in bulk. The conversation also touches on the psychological aspects, emphasising the need for dietitians to be empathetic and understanding of the challenges families face. Harriet encourages open communication and tailoring advice to individual circumstances. The podcast concludes with a discussion of resources, including local food banks and grants, that can provide additional support to families struggling with the cost of blended diets. Listen to the full podcast episode to learn more blended diets in paediatric enteral nutrition. We also have a number of webinars on blended diets which you can watch to learn more and a further podcast on blended diets in transitional care.
Information for Healthcare Professional Use Only In this episode of the Inside Medical Nutrition podcast, Dr. Linia Patel speaks with Lydia Collins Hussey, a specialist paediatric dietitian, about complementary feeding, weaning and allergen introduction for infants with food allergies. The conversation delves into recent trends in food allergies, highlighting the need to translate research into clinical practice and policy. Lydia mentions the importance of maternal diets, the microbiome, and early allergen introduction. Cows’ milk allergy is identified as the most common, followed by egg and peanut allergies. Lydia outlines the process of managing a child with suspected allergies, including taking a detailed allergy-focused history, assessing symptoms (immediate vs. delayed), and considering family history and eczema. The podcast then answers the question ‘What is complementary feeding’ and Lydia provides guidance around commencing weaning. This includes the numerous considerations that should be made regarding the safe commencement of weaning as well as the significance of food allergy management and early allergen introduction. For children with food allergies, Lydia advises starting allergen introduction between four and six months, especially for those with severe eczema or pre-existing allergies. She recommends introducing allergens in small amounts, mixing them with breast milk or formula, and ensuring the child is well during introduction. She also highlights the importance of maintaining tolerance by regularly including allergens in the diet. Listen to the full podcast to learn more about complementary feeding, weaning and allergen introduction for infants with food allergies. You may also be interested in this podcast with a specialist paediatric dietitian on managing enteral nutrition patients in the community. IMPORTANT NOTICE: We believe that breastfeeding is the ideal nutritional start for babies and we fully support the World Health Organisation’s recommendation of exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months of life followed by the introduction of adequate nutritious complementary foods along with continued breastfeeding up to two years of age. We also recognise that breastfeeding may not be an option due to certain medical conditions. Parents should only feed Infant formula for special medical purposes under supervision of a healthcare professional after full consideration of all feeding options, including breastfeeding. Continued use has to be assessed by the healthcare professional in relation to the baby's progress bearing in mind any social and financial implications for the family. Infant formula should always be prepared, used and stored as instructed on the label in order to avoid risks to a baby’s health.
Dr Rosan Meyer, a Paediatric Dietitian, discusses the Cow’s Milk related Symptom Score (CoMiSS) and how it can help healthcare professionals to be more aware of symptoms related to Cow’s Milk Allergy (CMA) and support the diagnosis of CMA. You can access the CoMiSS tool here. Information for Healthcare Professional Use Only
Information for Healthcare Professional Use Only In this episode of the Inside Medical Nutrition podcast, Dr. Linia Patel interviews Simon Williams, chief executive of Anaphylaxis UK, to discuss the organisation's role in supporting individuals and families affected by serious allergies. The conversation emphasises Anaphylaxis UK's comprehensive support system, encompassing information, training, and a helpline. The organisation aims to improve every aspect of life for those with allergies, from school and work to dining out. Simon stresses the importance of creating a welcoming environment for individuals with allergies, particularly in the food industry. The podcast addresses the rising prevalence of allergies, especially among children such as peanut allergy and cows’ milk allergy, and the need for increased awareness and procedures in schools. While the exact cause of this increase remains unclear, Anaphylaxis UK focuses on providing resources and training to ensure the safety of those living with allergies and at risk of anaphylaxis. Simon highlights the organisation's extensive online resources, including fact sheets reviewed by clinical experts and lay members. Anaphylaxis UK is also developing video and audio support for these resources to enhance accessibility. The organisation actively engages with the public through social media and a newsletter, providing updates on research, innovations, and product allergy alerts. A key focus of Anaphylaxis UK is addressing the significant anxiety experienced by individuals with allergies and their families. Simon emphasises the importance of creating a supportive environment and working with businesses to implement allergy-friendly practices. He introduces the Business Forum, bringing together major brands to improve standards and communication. The organisation also collaborates with suppliers to ensure the safety and availability of allergy-friendly products. Simon stresses the need for a "no-blame culture" to learn from mistakes and improve allergy management. To learn more about the role of Anaphylaxis UK in allergy management and support listen to the full podcast episode. You may also be interested in this podcast with a specialist paediatric dietitian discussing weaning and allergen introduction.
Information for Healthcare Professional Use Only In this episode of Inside Medical Nutrition, Dr. Linia Patel interviews Jacqui Lowdon, a paediatric specialist dietitian, about managing enteral nutrition patients in the community. Jacqui shares her journey into paediatric dietetics, starting with an interest sparked during a placement at a children's hospital. She discusses her current role as a clinical specialist in cystic fibrosis (CF) and her involvement with the British Dietetic Association. The conversation delves into current trends in enteral nutrition, noting an increase in children with respiratory issues requiring long-term ventilation and tube feeding. Jackie explains the criteria for choosing a feed, considering factors like the duration of feeding, the patient's ability to take oral diets, and potential underlying conditions. She emphasises the importance of understanding the patient's overall nutritional needs and tolerance to support enteral feeding at home for children. Jacqui highlights the evolution of available enteral feed formulas, from basic whole protein options to more specialised choices like fibre-containing, lower calorie, higher calorie, whey-based, and peptide-based feeds. She explains the use of peptide feeds for children who don't tolerate whole protein feeds and high-calorie feeds for those with high energy needs or limited tolerance for large volumes. The discussion emphasises the crucial role of parents and carers in decision-making. Jacqui stresses the importance of open communication, considering cultural backgrounds and religious beliefs. She shares a case study illustrating the challenges of convincing resistant parents to switch feeds, ultimately succeeding through persistence and a bit of luck. Jacqui's key takeaways include getting to know the patient and family, involving parents in discussions about enteral feeds, and recognising that enteral feed regimes can and should adapt to changing needs. She recommends utilising case studies and consulting with other dietitians to gain practical insights and support. She also stresses the importance of working with the family's routine and considering the child's whole day, not just the feeding schedule. Listen to the full episode to learn more about managing enteral nutrition patients in the community. You may also be interested in listening to this episode about using peptide feeds with enteral nutrition patients.
In this podcast Timira Naicker walks us through her journey as a dietitian and how she made the transition into the field of regulatory. Timira gives us great insights about her regulatory dietitian role, what are her interests, what does a typical day looks like and how you can think about a career in regulatory. Disclaimer: BDA endorsement applies only to the educational content of the learning activity.Information for Healthcare Professional Use Only
In this podcast Dr Michelle Harvie discuses the importance of research and setting research questions to test a hypothesis. One particular interesting area of work researched by Michelle is the very low-calorie diet and the 5:2 diet within diabetes. Disclaimer: BDA endorsement applies only to the educational content of the learning activity.Information for Healthcare Professional Use Only
In this podcast Dr Graeme O’Connor discusses his role as a research dietitian and how he made his first research move in the field of refeeding syndrome. After the success of developing clinical guidelines for the management of refeeding syndrome, Graeme went onto to research tube feeding formula containing food derived ingredients at Great Ormond Street Hospital. Graeme also highlights how dietitians can work with industry to test important questions such as 'how can a blended diet work in a hospital setting?' Disclaimer: BDA endorsement applies only to the educational content of the learning activity.Information for Healthcare Professional Use Only
In this podcast Dimitrios Koutoukidis discusses his journey as dietitian from Greece and now in the United Kingdom. His master’s degree enabled him to move into the field of research and is now working on some fantastic research that may support non-alcoholic fatty liver patients in the future. Disclaimer: BDA endorsement applies only to the educational content of the learning activity.Information for Healthcare Professional Use Only
In this podcast Annina Whipp walks us through her experiences as a paediatric and freelance dietitian. What excites her about her role, her interests and the types of projects she gets involved in. Disclaimer: BDA endorsement applies only to the educational content of the learning activity.Information for Healthcare Professional Use Only
Annina Whipp joins us to talk about the ins and outs of setting up a blended diet service. For some, this process isn’t straightforward and there may be several obstacles in the way and things you may not have considered. Annina shares her experiences and reflects on the whole process, sharing her words of wisdom and some helpful tips for others thinking about setting up their own service. Information for Healthcare Professional Use Only
Information for Healthcare Professional Use Only In this episode of the Inside Medical Nutrition podcast, Dr. Linia Patel interviews Ibrahim Amin, a lead practice pharmacist, about his experience managing cow’s milk protein allergy (CMPA). Ibrahim shares his journey into pharmacy, driven by a love for chemistry and a desire for patient contact. The conversation explores the pharmacist's role in cow’s milk protein allergy (CMA) management, emphasising that it extends beyond dispensing prescriptions. Ibrahim discusses supporting patients and healthcare professionals, conducting audits, and ensuring adherence to guidelines. He highlights the importance of recognising that pharmacists are medicine experts and can provide valuable advice. Ibrahim notes a concerning trend of delayed diagnoses and inappropriate management of CMA, often stemming from initial visits to A&E. He stresses the need for accurate diagnoses, appropriate formula prescriptions, and ongoing monitoring of patients. He discusses some of the common symptoms of cow’s milk allergy such as rashes and gastrointestinal symptoms. The discussion delves into the importance of communication and collaboration within a multidisciplinary team. Ibrahim emphasises the value of virtual MDT meetings, which improve efficiency and accessibility. Ibrahim shares practical tips for managing CMA, including reminding parents that "breast is best" and providing guidance on dairy-free diets for mothers who are breastfeeding. The podcast concludes with a call for pharmacists to be proactive in supporting GPs and patients with CMA, emphasising the need for continuous review, accurate diagnoses, and a patient-centred approach. Ibrahim's insights shed light on the crucial role pharmacists play in optimising CMA management and improving patient outcomes. Listen to the full podcast episode to learn more about the role of pharmacists in cow’s milk allergy diagnosis and management. IMPORTANT NOTICE: We believe that breastfeeding is the ideal nutritional start for babies and we fully support the World Health Organisation’s recommendation of exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months of life followed by the introduction of adequate nutritious complementary foods along with continued breastfeeding up to two years of age. We also recognise that breastfeeding may not be an option due to certain medical conditions. Parents should only feed Infant formula for special medical purposes under supervision of a healthcare professional after full consideration of all feeding options, including breastfeeding. Continued use has to be assessed by the healthcare professional in relation to the baby's progress bearing in mind any social and financial implications for the family. Infant formula should always be prepared, used and stored as instructed on the label in order to avoid risks to a baby’s health.
Managing the nutrition and hydration needs of dysphagia patients in the care home setting can be challenging. Sophie Murray Quality Improvement and Regulatory Partner for Signature Care Homes sits down with Linia to discuss optimal management and the positive impact this can have on patient outcomes. Information for Healthcare Professional Use Only
Information for Healthcare Professional Use Only In this episode of the Inside Medical Nutrition podcast, Dr. Linia Patel interviews Claire Thornton-Wood, a paediatric dietitian, about Avoidant Restrictive Food Intake Disorder (ARFID). ARFID is a relatively new diagnosis, recognised in 2013, that encompasses various previous conditions like infantile anorexia and extreme selective eating. It is categorised as an eating disorder, however, unlike other eating disorders, ARFID is not related to body image concerns. Claire emphasises that ARFID is a mental health diagnosis with significant physical implications. It affects both children and adults, with a possible family link. Claire explains that ARFID is characterised by a pattern of avoiding certain foods or food groups, restricting quantities, and not being influenced by body image. The United States Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) criteria include persistent failure to meet nutritional needs, leading to weight loss, nutritional deficiencies, dependence on feeding tubes or supplements, and interference with psychosocial functioning. Predisposing factors include choking episodes, medical conditions causing gagging, tube feeding history, and aversive experiences with medication. The longevity and severity of symptoms of ARFID differentiate this condition from picky eating. Diagnosis of ARFID can be made in both adults and children, with ARFID in children being diagnosed as early as 2 years. The journey to diagnosis can be significant for some children. The impact on families is substantial, causing anxiety about nutrition, social difficulties, and challenges in school. Management involves ensuring nutritional safety, reassurance, and addressing weight concerns. Dietitians may recommend vitamin and mineral supplements, oral nutritional supplements, and fortified foods. In severe cases, tube feeding may be necessary. The end goal is a happy, healthy child and family, with minimal impact on their lives and reduced anxiety. Claire advises healthcare professionals to be alert to ARFID, curious about it, and encouraged by the growing awareness and training in this area. Listeners can find more information on the DSM criteria online, the British Dietetic Association website, and the Nestle N+ Hub. To learn more about the diagnosis and management of ARFID in paediatrics listen to the full episode. Listen to our other episodes of the Inside Medical Nutrition podcast on a range of clinical nutrition topics.
In this podcast Lisa Philips-German, a Paediatric Nurse Consultant talks us through her unique role and how she successfully manages cows’ milk allergy patients in her paediatric community. Lisa will share the success of her clinic and how they have managed to empower and support parents and carers, work with other healthcare professionals and strengthen service provision in the community. Important notice: Mothers should be encouraged to continue breastfeeding even when their infants have cows' milk protein allergy. This usually requires qualified dietary counselling to completely exclude all sources of cows' milk protein from the mothers’ diet. Information for Healthcare Professional Use Only
Dysphagia Chef Gary Brailsford and Independent Dietitian Caroline Hill sit down to discuss texture modified diets. From myth busting to best practice, they explore how to texture modified diets right, for your dysphagia patients. IDDSI Framework * For healthcare professionals only.
Information for Healthcare Professional Use only In this episode of the Inside Medical Nutrition podcast, Dr. Linia Patel hosts a discussion with Sandra Robinson, a speech and language therapist, and Caroline Hill, a dietitian, about the importance of a multidisciplinary team (MDT) approach in managing patients with dysphagia. The discussion begins by defining the different types of teamwork: multidisciplinary, interdisciplinary, and transdisciplinary. The guests emphasise the value of an interdisciplinary approach (IDT), where team members actively collaborate and communicate to provide coordinated care. They contrast this with a multidisciplinary approach, where professionals work independently with less interaction. The podcast highlights the diverse members of an MDT, including physicians, nurses, therapists, assistants, chefs, and, importantly, the patients and their families. They discuss how MDTs function in primary care and the role of specialist nurses in bridging communication gaps. The conversation explores the impact of COVID-19 on dysphagia management, particularly the increased reliance on telehealth. While telehealth offers benefits, it also presents challenges, such as ensuring patient safety, relying on facilitators, and addressing communication barriers. Best practices for virtual consultations include being prepared with technology, supporting patients and facilitators, and setting clear expectations. The guests stress the importance of ongoing education and awareness of dysphagia, suggesting that speech and language therapy training should begin at the undergraduate level. They also propose considering a title like "dysphagia practitioner" to better reflect the scope of practice. The key takeaways of effective dysphagia management are the importance of communication, education, and a patient-centered approach. The guests encourage healthcare professionals to work closely together, understand each other's roles, and prioritise the needs, wishes, and preferences of the individual with dysphagia. They conclude that effective teamwork is essential for optimising nutrition, hydration, and overall quality of life for patients with swallowing difficulties. To learn more about the importance of a multidisciplinary team (MDT) approach in managing patients with dysphagia, listen to the full episode. You may also be interested in this Inside Medical Nutrition podcast episode on medication administration in dysphagia.
Once the decision has been made to start a child on a blended diet, it’s never the dietitian alone who is responsible for supporting this. The entire multi-disciplinary team needs to be aligned and working closely together to help support this patient. Harriet Farr talks us through the role of the MDT in supporting blended diets and how this is best structured, communicated and monitored. Information for Healthcare Professional Use Only
Information for Healthcare Professional Use onlyIn this episode of the Inside Medical Nutrition podcast, Dr. Linia Patel interviews Carol Baguley, a paediatric dietitian, about managing blended diets in a school setting. Carol shares her journey from South Africa to becoming a specialist in paediatric nutrition in the UK. Carol's current role involves providing optimal nutrition to children with neuro disabilities at a specialist school. She manages a caseload of around 80 children, many of whom are home enteral feeding (HEF) dependent, with a significant portion also consuming blended diets. The conversation highlights the practicalities of managing blended diets in schools, including food preparation, storage, and hygiene. Carol emphasises the importance of a blended diet policy, which is followed meticulously. Staff training is crucial, with school nurses playing a key role in educating carers and parents. The discussion touches on the importance of individualising blended diets and considering factors like texture and nutrient content. Carol also mentions the use of fortified foods and specialised plant-based alternatives creams to enhance nutritional value. Consideration is also given to the care of feeding tubes for those individuals receiving a blended diet. Carol encourages listeners to consult the British Dietetic Association (BDA) and the Food Standards Agency (FSA) for further information. She concludes by emphasising the positive impact of blended diets on children's well-being and the importance of a collaborative approach to care. Carol discusses the impact of blended diets on children's quality of life, noting improvements in reflux, bowel habits, and social interaction. She shares a case study of a 17-year-old boy who transitioned to a 100% blended diet after numerous challenges with enteral feed intolerance, resulting in improved bowel habits, reduced vomiting, and better weight gain as well as an increase in social interactions. Looking to the future, Carol believes blended diets are gaining popularity and emphasises the need for more resources and training. She highlights the importance of shared decision-making, involving all stakeholders, including schools, in developing training and policies. Listen to the full episode to learn more about the practicalities of managing a blended diet. For more information about blended diets watch these webinars on the N+ hub.
Information for healthcare professional use onlyIn this episode of the Inside Medical Nutrition Podcast, Dr. Linia Patel discusses the tolerance of blended diets with experts Lucy Jackman, a paediatric dietitian, and Dr. Graham O'Connor, a research lead for dietetics, both from Great Ormond Children's Hospital. The conversation begins with the experts sharing their backgrounds and their journey into dietetics. The discussion then shifts to the increasing use of blended diets, which are household foods blended into a liquid form for tube feeding. Parents are increasingly drawn to blended diets due to a desire for natural food and the feeling of fulfilling their role as caregivers. The experts address concerns about blended diets, including tube blockages, nutritional adequacy, and food hygiene. Research suggests that in practice, these concerns are not significantly different compared to commercial formulas. Key considerations for blended diets include using appropriate tube sizes, avoiding nasogastric (NG) tubes, ensuring proper consistency, and maintaining food safety standards. The podcast explores the role of food-derived ingredient formulas as a middle ground between blended diets and commercial formulas. The speakers share their experience of using these formulas and how they can be particularly useful in hospital settings where providing fresh blenderised food is challenging. They also offer a way to control electrolytes and provide fibre, which is beneficial for gut health, both of which is particularly important in intensive care patients. The experts emphasise the importance of individualised patient care and monitoring when using blended diets or formulas with food-derived ingredients. This includes assessing macronutrient and micronutrient intake, tracking growth parameters, and potentially monitoring nutritional blood levels.Looking to the future, the experts express optimism about the role of blended diets and formulas with food derived ingredients in dietetic care. They highlight the potential for these approaches to improve patient outcomes and quality of life. Listen to the full episode to learn more about the tolerance of tube fed blended diets. For more information about blended diets watch these webinars on the N+ hub.
Information for healthcare professional use only In this episode of the Inside Medical Nutrition Podcast, Dr. Linia Patel interviews Catherine Fogarty, a paediatric dietitian, about managing a tube-fed blended diet caseload. Cath shares her journey from being a chef to a dietitian, highlighting her passion for food and nutrition. She currently manages a caseload of 100 tube-fed children, with approximately 15% on blended diets. Cath discusses the evolution of blended diet acceptance, noting the positive impact of the British Dietetic Association's policy statement in 2019. She emphasises the importance of a collaborative approach with parents, involving them in the decision-making process and providing education on food safety, preparation, and nutritional adequacy. She outlines the challenges of managing a blended diet caseload, particularly with children who have neurological impairments or food aversions. Cath emphasises the need for a holistic approach, considering factors beyond the feed itself, such as the gut-brain axis and the child's social environment. Cath shares strategies for managing her time, including prioritising urgent cases, utilising virtual consultations, and seeking support from colleagues and professional organisations like DISC (Dietitians Interested in Special Children). She stresses the importance of starting slowly with blended diets, treating it like weaning, and empowering parents to make informed choices. Cath highlights the need for more resources and guidance for dietitians managing blended diet caseloads, including safe caseload recommendations and recipe books tailored to specific needs. She encourages dietitians to embrace blended diets as a valuable tool for improving the nutrition and quality of life for tube-fed children, while always prioritising food safety and individual patient needs. Listen to the full episode to learn more about managing a caseload of patients using blended diets.
Clare Thornton-Wood shares her experience of supporting children with blended diets and discusses why they are becoming more popular amongst parents and carers. Why are they preferred by some parents? How do they benefit the children and the family? And how can dietitians themselves ensure they are set up to support parents wishing to start a blended diet? Clare also talks through what the BDA has to say about blended diets with a look at their latest policy statement. Information for Healthcare Professional Use Only
Tune in and discover what’s in store in the first series of Inside Medical Nutrition, a podcast powered by Nestlé Health Science. Information for Healthcare Professional Use Only
To read and download the case study click here. To read more on the nutritional profile for Peptamen Junior 0.6 click here. Further reading Management of weight gain in tube-fed children with neurodisabilities Weight Gain in Tube-Fed Neurodisability Children
To read and download the case study click here. To read more on the nutritional profile for Peptamen Junior 0.6 click here. Further reading Management of weight gain in tube-fed children with neurodisabilities Weight Gain in Tube-Fed Neurodisability Children
To watch a full webinar on case studies for Peptamen Junior 1.5kcal/ml ONS, from the Acceptability and Tolerance Study, click here. To read and download the case study click here. To read more on the nutritional profile for Peptamen Junior 1.5 click here.
To watch a full webinar on case studies for Peptamen Junior 1.5kcal/ml ONS, from the Acceptability and Tolerance Study , click here. To read and download the case study click here. To read more on the nutritional profile for Peptamen Junior 1.5 click here.
To read and download the case study click here. To read more on the nutritional profile for Peptamen Junior 0.6 click here. Further reading Management of weight gain in tube-fed children with neurodisabilities Weight Gain in Tube-Fed Neurodisability Children
To read and download the case study click here. To read more on the nutritional profile for Peptamen HN click here. Further reading Another case study for Peptamen HN to read and download , click here
To read and download the case study click here. To read more on the nutritional profile for Peptamen HN click here. Further reading C.Dejong; F. Hammargyist et al. ESPEN guidelines on enteral nutrition: gastroenterology. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition Voulme 25, Issue 2. 2006. Pages 260-274. Henry CJK. Basal metabolic rate studies in humans: measurement and development of new equations. Public Health Nutrition 2005; 8 (7A): 1113-1152. Thomas B & Bishop J (Eds.) Manual of Dietetic Practice 4th edition. Blackwell Publishing Ltd; Oxford 2007, pp475-477. K, Spiroglou et al. Gastric emptying in children with cerebral palsy and gastroesophageal reflux. Paediatric Neurology 2004; 31 (3):177-182.
To read and download the case study click here. To read more on the nutritional profile for Peptamen AF click here. Further reading Motor Neurone Disease Association. www.mndassociation.org National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE), (2016). Motor Neurone Disease: Assessment and Management. Available at: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng42/resources/motor-neurone-disease-assessment-and-management-1837449470149. Ng L, Khan F. Multidisciplinary care for adults with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis or motor neuron disease. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2009, Issue 4. Art. No.: CD007425. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD007425.pub2.
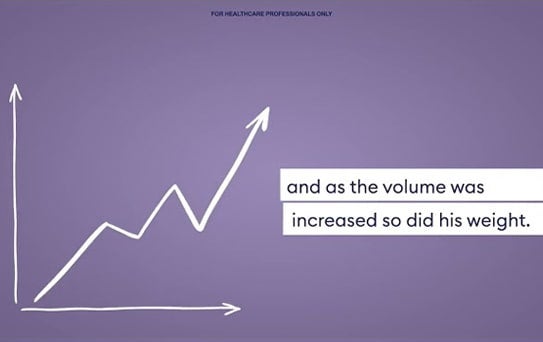
Watch if an enteral tube feed containing food-derived ingredients can improve both the physical health and mental wellbeing of an adult patient. Switching to an enteral tube feed containing food-derived ingredients helped Patient X’s physical health and management, and resulted in great psychological benefits.
To read and download the case study click here. To read more on the nutritional profile for Peptamen Junior 0.6 click here. Further reading Management of weight gain in tube-fed children with neurodisabilities Weight Gain in Tube-Fed Neurodisability Children