Background
Cows’ milk allergy (CMA) is one of the major food allergies during infancy and childhood.
Hypoallergenic formulas can be necessary for managing infants and children with severe CMA. According to the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), a formula is “hypoallergenic” if it does not provoke allergenic activity in 90% of infants or children with confirmed CMA with 95% confidence in a double-blind placebo-controlled food challenge (DBPCFC) as compared to a commercially available hypoallergenic formula. After a successful DBPCFC, a week-long open challenge is recommended to confirm lack of allergic symptoms during prolonged feeding.
A new amino acid-based nutritionally complete infant formula (AAF) designed for the management of severe CMA and intolerance has been developed.
Objective
Primary objective: To determine whether a new AAF is hypoallergenic as defined by AAP criteria.
Secondary objectives: To examine the digestive tolerance and document any symptoms of potential allergic etiology in subjects who consume the new AAF during an open feeding challenge over 7-9 days.
Methods
Children (2 months to ≤ 12 years of age) with confirmed (within 6 months of enrollment) CMA participated in a multi-centre clinical trial of DBPCFC with a new AAF (Test) and a commercially available AAF (Control) in a randomised, crossover fashion over a 2-7 day period.
Subjects were monitored during the DBPCFCs for immediate allergic reactions via a rigorous and comprehensive scoring system and observed for a minimum 1 hour prior to discharge.
If both blinded challenges were tolerated, subjects participated in a week-long open challenge of a minimum 8 ounces daily intake of the Test formula at home. Formula intake, stool characteristics, incidence of flatulence, emesis and spit-up were documented.
Results
- Overall, 37 subjects were randomized; 33 subjects completed both DBPCFC of the Test and Control AAFs (Figure 1).
- Demographic characteristics of study participants are presented in Table 1.
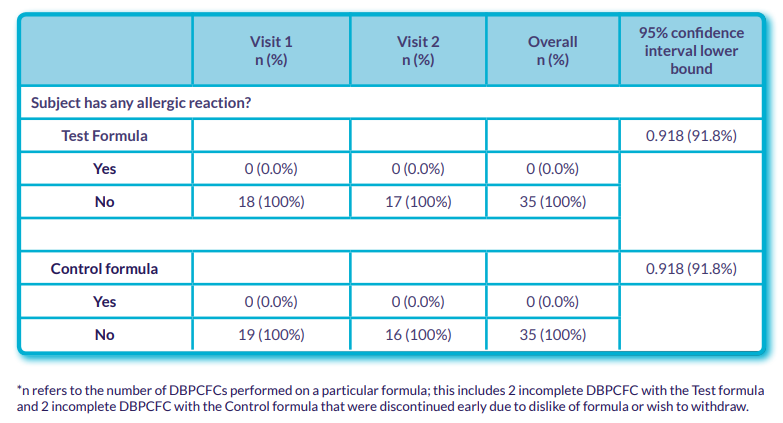
- No subjects had an acute allergic reaction to either formula during DBPCFC (Table 2).
- 33 subjects participated in the week-long at-home open feeding challenge.
- 30 subjects consumed at least 8 oz of formula for 5 days; average intake was 9.6±5.2 oz/day.
- 4 subjects vomited during the open challenge but continued formula intake at home and completed the week-long open challenge; vomiting was attributed to palatability issues. These symptoms were not reported as adverse events.
- One subject reported erythema around the mouth which only lasted a few minutes on one day of the open challenge. Another subject reported itchy skin on back for 5 days of the open challenge. These symptoms were not reported as adverse events.
- One subject reported abdominal pain (a mild “stomach ache”) on 4 days of the open challenge, each of which resolved on the day it started and was deemed as having a probable relation to study product.
Conclusions
The new test amino acid-based formula meets the American Academy of Pediatrics criteria for hypoallergenicity and can be recommended for the management of cows’ milk allergy.
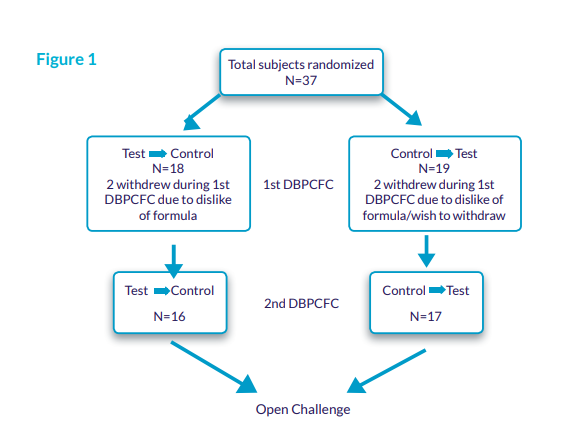
Table 1 - Demographic information
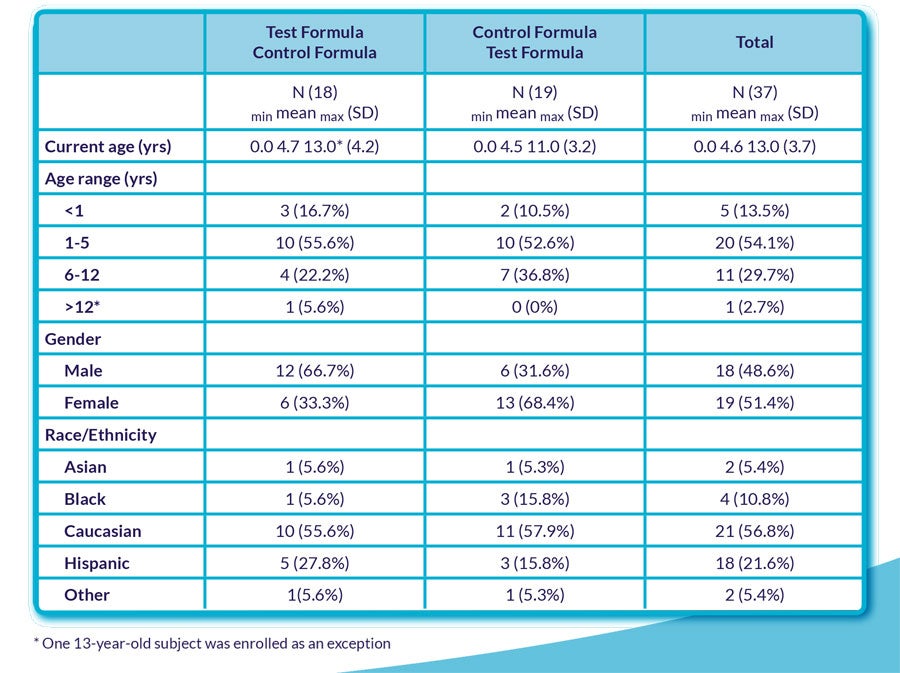
Table 2
IMPORTANT NOTICE: Mothers should be encouraged to continue breastfeeding even when their infants have cows’ milk protein allergy. This usually requires qualified dietary counselling to completely exclude all sources of cows’ milk protein from the mothers’ diet. If a decision to use a special formula intended for infants is taken, it is important to give instructions on correct preparation methods, emphasising that unboiled water, unsterilised bottles or incorrect dilution can all lead to illness. Formula for special medical purposes intended for infants must be used under medical supervision.
Cows’ milk allergy (CMA) is one of the major food allergies during infancy and childhood. Hypoallergenic formulas can be necessary for managing infants and children with severe CMA. According to the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), a formula is “hypoallergenic” if it does not provoke allergenic activity in 90% of infants or children with confirmed CMA with 95% confid...